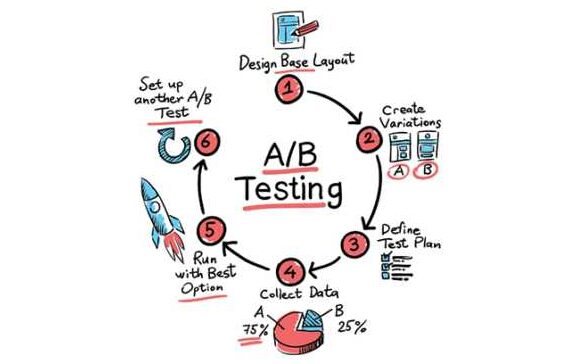
Data-driven decision-making stands at the forefront of success. A/B testing, also known as split testing, is a powerful tool that empowers businesses to optimize their products through rigorous experimentation and analysis. By comparing different variations of a product or feature, A/B testing helps teams identify the most effective strategies that resonate with their target audience. This article will explore how A/B testing can significantly enhance the product analytics process, enabling organizations to make informed decisions, improve user experiences, and drive sustainable growth.
Understanding A/B Testing
A/B testing is a controlled experiment where two or more variations of a product or feature are presented to users simultaneously, and their interactions and behaviors are measured. One group of users is exposed to the original version (control), while others experience the modified version(s) (variants). The goal is to determine which variant performs better based on predefined metrics and objectives.
How A/B Testing Enhances Product Analytics
A/B testing plays a critical role in the product analytics process, complementing other data analysis techniques. Here’s how A/B testing enhances product analytics:
- Unbiased and Controlled Experiments:
A/B testing eliminates bias by ensuring that users are randomly assigned to different variations. This controlled experimentation allows businesses to attribute any differences in user behavior to the changes made in the variants, providing more accurate and reliable insights.
- Data-Backed Decision-Making:
A/B testing helps organizations make data-backed decisions. By quantifying the impact of each variant on specific metrics, product teams can confidently choose the version that best aligns with their objectives, rather than relying on gut feelings or assumptions.
- User Behavior Insights:
A/B testing provides valuable insights into user behavior. By monitoring user interactions and actions within each variant, businesses can understand how users engage with different elements and features of the product.
- Iterative Product Improvement:
A/B testing fosters an iterative approach to product development. Teams can continuously experiment with new ideas and variations, iterating on improvements based on data-driven insights to enhance the product over time.
- Measurable Outcomes:
A/B testing enables the measurement of outcomes and the evaluation of product performance against predefined metrics. This ability to measure results makes it easier to set achievable goals and track progress toward them.
A/B testing allows businesses to segment users based on different characteristics or behaviors, such as new versus returning users or different user personas. This segmentation provides a deeper understanding of how specific user groups interact with the product.
How to Implement A/B Testing in the Product Analytics Process
To successfully implement A/B testing and unlock its potential in the product analytics process, businesses can follow these steps:
- Define Clear Objectives:
Clearly outline the objectives of the A/B test. Identify the specific metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) that will determine the success of each variant. For example, if the goal is to increase user engagement, metrics like time spent on page or click-through rates may be relevant.
- Identify Test Variables:
Determine the elements or features that you want to test within the variants. These variables could include changes to the user interface, design elements, calls-to-action, or pricing structures. Ensure that the variations are distinct enough to produce measurable differences in user behavior.
- Randomly Assign Users:
Randomly assign users to each variant to avoid bias. A robust A/B testing platform ensures that users have an equal chance of experiencing any of the variations, allowing for accurate comparisons between the control and the variants.
- Set Sample Size and Duration:
Determine the required sample size and the duration of the A/B test. Sufficient sample size ensures statistical significance, while the duration of the test should be long enough to capture different user behaviors over time.
- Implement Testing Mechanism:
Implement the A/B testing mechanism using an appropriate tool or platform. Several A/B testing tools, such as Google Optimize, Optimizely, or VWO, facilitate the setup and analysis of experiments.
- Monitor User Interactions:
Monitor and analyze user interactions and behavior within each variant. Track the predefined metrics to evaluate the performance of each variation against the objectives.
- Draw Conclusions:
Based on the test results, draw conclusions about the effectiveness of each variant. Identify the version that performs better in achieving the defined objectives.
- Implement Successful Variants:
Implement the successful variant as the new standard, optimizing the product or feature based on the insights gained from the A/B test.
- Iterate and Refine:
Continue the iterative process of A/B testing to further refine and improve the product. As user behaviors and preferences change, adapt the product to cater to evolving needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, A/B testing is a powerful tool that significantly enhances the product analytics process. By facilitating controlled experiments, A/B testing empowers businesses to make data-driven decisions, gain valuable insights into user behavior, and optimize user experiences. Measuring and comparing outcomes enables product teams to iterate and improve their offerings continuously. A well-executed A/B testing strategy complements other data analysis techniques, providing a comprehensive understanding of user interactions and product performance. Embracing A/B testing as an integral part of the product analytics process empowers organizations to stay agile, responsive to user needs, and drive sustainable growth in an ever-evolving digital landscape.